Before diving into how to setup cron jobs, let me explain what cron-jobs are and how they are useful in building systems. A cron job is some kind of scheduler which will run automatically at specific interval like hourly, daily, weekly, or at custom schedules.
Real-world Use Cases
- Sending daily emails - Charging subscriptions - Syncing data between systems
- Running backups - Cleaning expired data - Triggering long-running workflows
In simple terms any repetitive task we want to do at a specific interval, we set up a cron job for it.
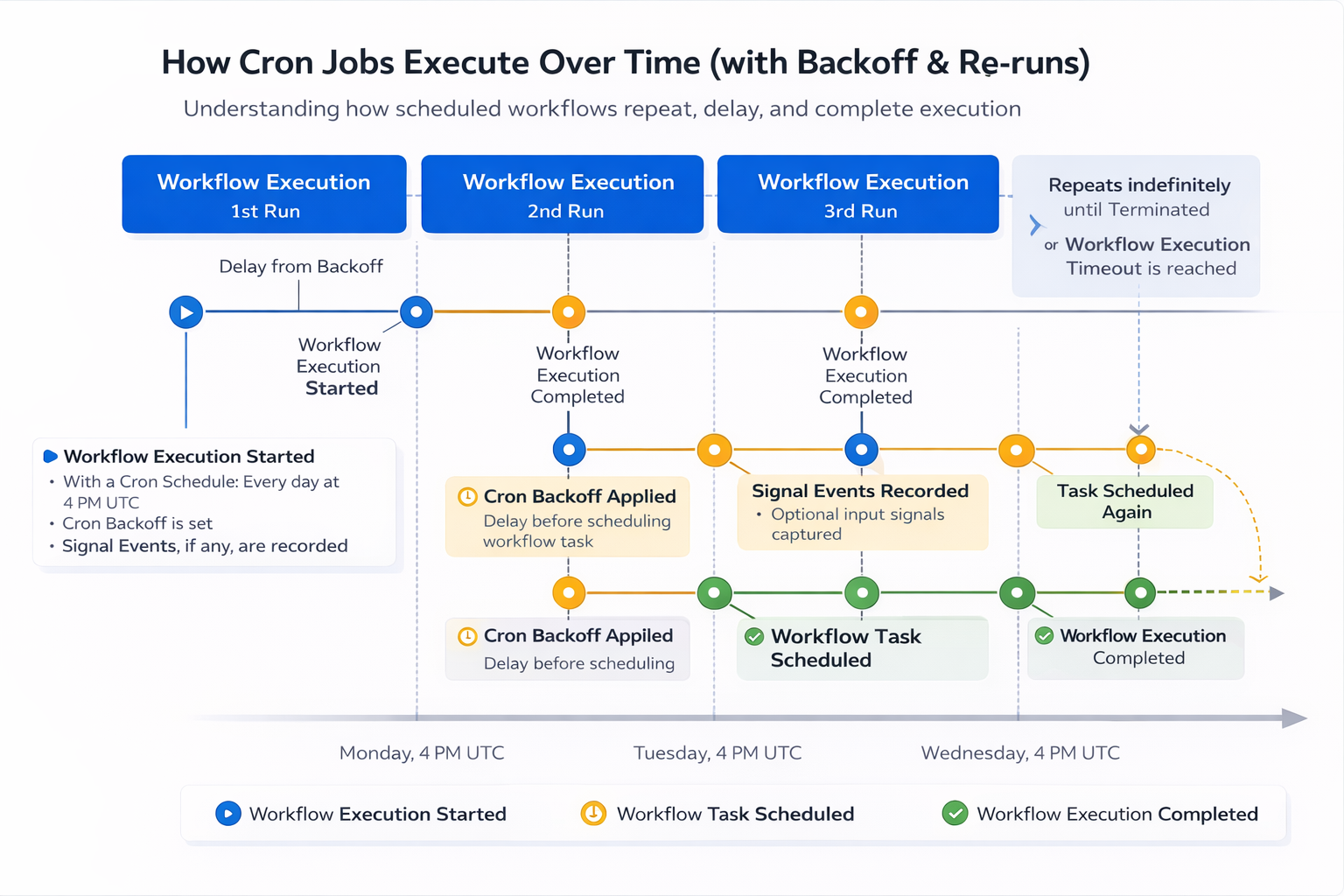
Cron is not about when something runs it's about guaranteeing that it eventually does, even when things fail.
Why Nextjs Can't run Cron-jobs by default?
It's not true that we can't run cron-jobs in nextjs it's entirely depends on where and how your next.js application is deployed. Most confusion around cron jobs exists because people mix up next.js with the infrastructure it runs on. Nextjs itself does not decide whether cron jobs work or not. the deployment model does. To understand this, you first need to know the difference between Serverless and a Serverful servers.
What is Serverless architecture
In a serverless architecture your app is not running all the time like our serverful servers. The server starts only when request received to server will be up and down once request is served. this means there is no long-running process that stay alive in background to run cron-jobs. Platforms like Vercel, Netlify, AWS lambda, and Cloudflare workers work this way.
What are Serverful Server
A serverful server is a server that runs continuously, twenty-four by seven. it does not shut down when there are no users. the node.js process stays alive, memory is preserved, and background tasks keep running.
Why node-cron does not work in serverless Next.js Cron jobs need a process that stays alive and keeps checking the current time. node-cron works by attaching itself to the node.js event loop and running tasks when the time matches a schedule. this works only if the process never stops.
In serverless environments, the process starts, handles one request, and then gets destroyed. so even if you register a cron job using node-cron, it runs only once during that request and then disappears. there is no error and no warning, which makes it confusing for beginners. the cron job does not fail it simply never had a chance to run. this is reason why using node-cron inside a next.js app deployed on Vercel, Netlify, or AWS Lambda does not work.
Serverful Examples: Running next.js on a virtual machine, inside a docker container, or using a process manager like pm2. In these setups, the application behaves like a traditional backend server because the process never stops.
So can next.js run cron jobs or not?
Short Answer: Yes next.js can run cron jobs, but only when it is deployed on a serverful server. Next.js running on serverless platforms cannot run cron jobs by itself because there is no always-running process.
Now that it's clear why Next.js behaves differently based on deployment, let's look at working code examples for both cases. The core idea is simple: in serverless, cron jobs are triggered from outside your app, while in a serverful server, cron jobs run inside your Node.js process.
Running cron jobs in Serverless NextJs App
When you are deploying your app in serverless architecture you need some kind of scheduler which can hit some endpoint at specific time in your application like Vercel. We have options like AWS Lambda and Amazon EventBridge Scheduler, or for Google cloud platforms like Cloud Functions or Pub/Sub.
Below example covers running cron job using Next.js API route + Vercel config file. To create a job we need to create an endpoint in our Next.js application:
// app/api/daily/route.tsimport { RefilUserCredits } from "@/api/user/credits";export function GET(request: Request) {console.log("CRON RAN AT:", new Date().toISOString());RefilUserCredits(); // a task which needs to perform like refilling tokensreturn new Response("Cron job running");}// app/api/daily/route.tsimport { RefilUserCredits } from "@/api/user/credits";export function GET(request: Request) {console.log("CRON RAN AT:", new Date().toISOString());RefilUserCredits(); // a task which needs to perform like refilling tokensreturn new Response("Cron job running");}
and create one vercel.json file at root of application
{"$schema": "https://openapi.vercel.sh/vercel.json","crons": [{"path": "/api/daily", // specify the api route you created"schedule": "0 0 * * *" // when you want to run this route}]}{"$schema": "https://openapi.vercel.sh/vercel.json","crons": [{"path": "/api/daily", // specify the api route you created"schedule": "0 0 * * *" // when you want to run this route}]}
now you are good to go just deploy you app this cron job will run in your application and perform action at specific time.
Logs of running cron job with time
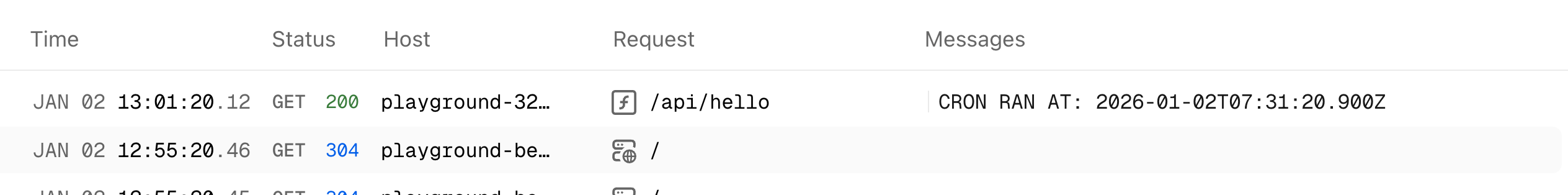 logs from vercel scheduler
logs from vercel schedulerServerful Server using node-cron
When your next.js app is deployed on a serverful server, the node.js process runs continuously. because the process never shuts down, you can safely register cron jobs using node-cron. the first step is to install the dependency.
npm install node-cronnpm install node-cron
now create a place where all cron jobs live. this code must run once when the server starts, not on every request. Create server.ts file in root directory of your application
export async function register() {// only run the the runtime is nodejsif (process.env.NEXT_RUNTIME === "nodejs") {const { initCronJobs } = await import("./app/server");// start cron jobs / serverinitCronJobs();}}export async function register() {// only run the the runtime is nodejsif (process.env.NEXT_RUNTIME === "nodejs") {const { initCronJobs } = await import("./app/server");// start cron jobs / serverinitCronJobs();}}
Environment check ensures that cron jobs start only when your app is running as a node.js server and not in edge or serverless runtimes.
This check is crucial to prevent cron jobs from trying to run in the Edge runtime where node-cron isn't supported.
inside app directory create server/index.ts file
import cron from "node-cron";import { createRoom } from "./room";const tasks: ReturnType<typeof cron.schedule>[] = [];export async function registerReportCron() {console.log("[Cron] Registering Report Cron...");// Original (Every minute): "0 \* \* \* \* "const task = cron.schedule("0 0 \* \* \*", async () => {console.log("[Cron] Report Job Triggered");try {await createRoom("anon-lion-gxn");} catch (error) {console.error("[Cron] Job execution failed:", error);}});tasks.push(task);console.log("[Cron] Report Job Scheduled (Runs every day at 00:00)");}export function initCronJobs() {registerReportCron();}import cron from "node-cron";import { createRoom } from "./room";const tasks: ReturnType<typeof cron.schedule>[] = [];export async function registerReportCron() {console.log("[Cron] Registering Report Cron...");// Original (Every minute): "0 \* \* \* \* "const task = cron.schedule("0 0 \* \* \*", async () => {console.log("[Cron] Report Job Triggered");try {await createRoom("anon-lion-gxn");} catch (error) {console.error("[Cron] Job execution failed:", error);}});tasks.push(task);console.log("[Cron] Report Job Scheduled (Runs every day at 00:00)");}export function initCronJobs() {registerReportCron();}
in this setup, next.js behaves like a traditional backend. as long as the server is up, cron jobs keep running in the background.
References:
Thank you for reading till the end.